|
|||
| >
ADAMLink
Home |
|||
|
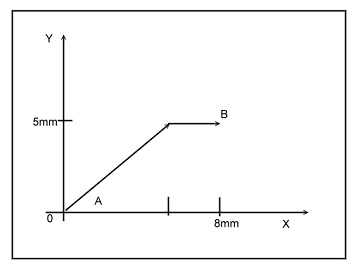
Point-to-point (PTP) motion Point-to-point (PTP) motion is the most basic form of motion control. It is used when precise start and stop position is important, but the path is irrelevant. In a PTP movement from point A to point B, the motors for the Y and X axes will move at the same speed, so as you can see in the diagram below, the motor for Y arrives at its destination before X, and then stops. X still has to move 3 mm, so it arrives later. The result is a path that looks like a broken line. But the path is irrelevant in this example; it is the position that matters. Point-to-Point motion . Linear and
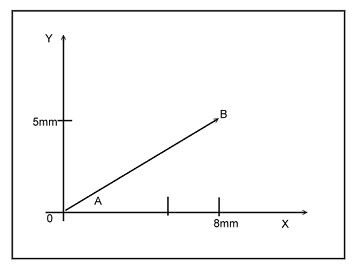
Circular Interpolation Linear Interpolation
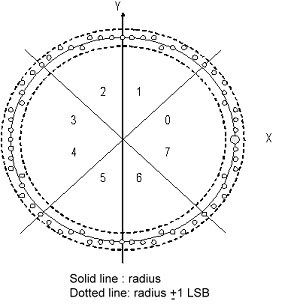
For circular interpolation two synchronous motors follow a path that is based on parameters for a circle: the circle's radius, start angle and travel angle. The radius is the arc radius in counts for servo axes or steps for stepper axes. The start angle is a number between 0 and 360°, where 0 is along the positive X axis. Increasing the value moves the position counter-clockwise along the radius. The travel angle is the value in degrees to be traversed, so a positive travel angle would mean counter-clockwise movement, while a negative travel angle would mean clockwise movement. Circular Interpolation
Continuous
and Non-Continuous Interpolation In the second application, you need to drill four holes along the path. So this time, you want the motors to stop when reaching a point, wait for the drill to finish, and then move to the next point. This is the situation that non-continuous interpolation is used for. When the motors start moving from point A to point B, the controller will speed up to the highest speed, then slow down and stop when it arrives at point B, do the drilling, and then speed up again as it continues to point C. By using the right kinds of interpolation for your application, you can achieve more precise motion control and also give less stress to your motors. |
|||
|
. |
|||
|
Advantech
Industrial Automation ADVANTECH
Automation 1320 Kemper Meadow Dr., Ste 500, Cincinnati, OH 45240.
877-294-8989 |
|||